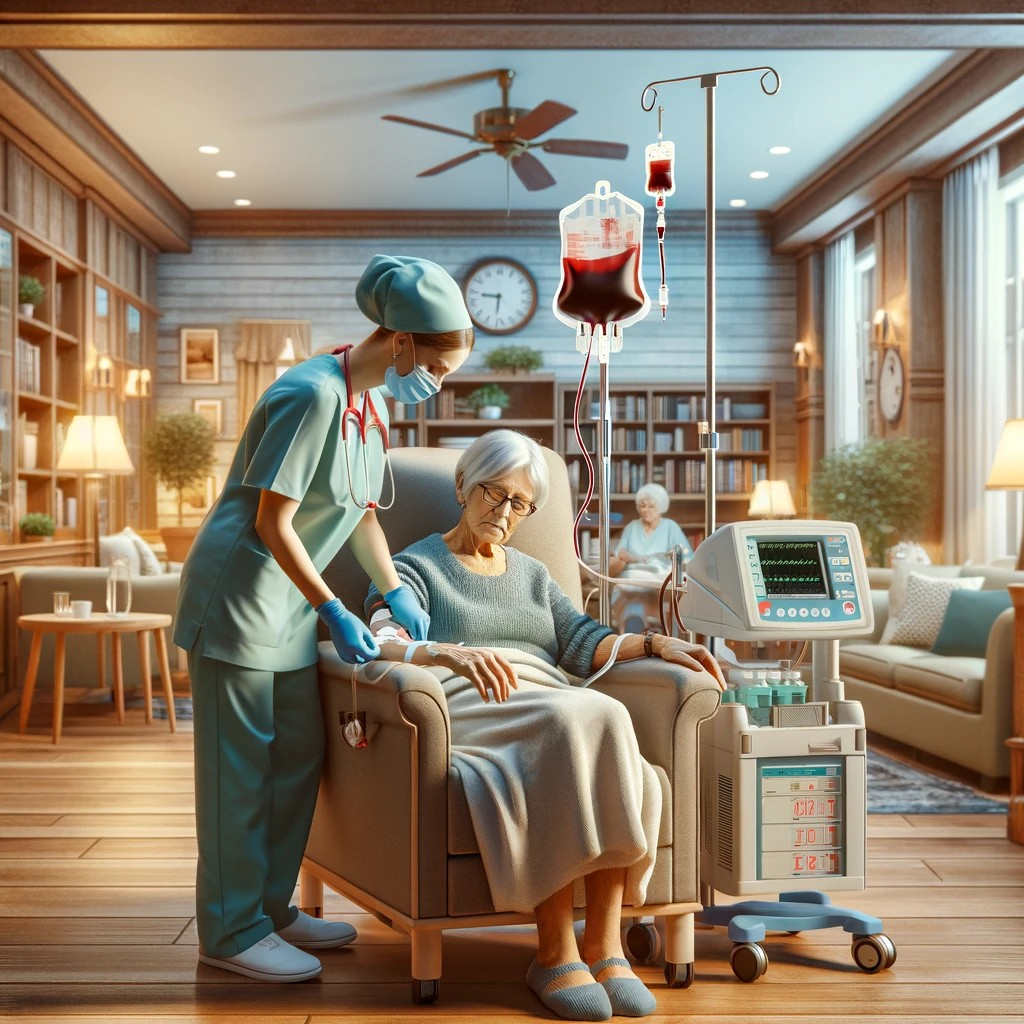
c. Treatment: Transfusion- On Adm, Step-by-Step
Step-by-Step Coding Guide for Item Set: O0110I1a, Treatment: Transfusion- On Admission
1. Review of Medical Records
Objective: Identify if a transfusion was administered upon admission. Key Points:
- Thoroughly review the resident's medical records upon admission for any documented transfusions.
- Focus on physician orders, nursing assessments, and medication administration records (MARs) that detail the transfusion of blood products.
- Note the type of blood product transfused (e.g., whole blood, packed red blood cells, platelets), including dosage, administration time, and duration.
2. Understanding Definitions
Objective: Define what constitutes a transfusion treatment. Key Points:
- A transfusion involves the administration of blood or blood products into one's circulation intravenously.
- Transfusions are performed to replace lost components of the blood, commonly due to surgery, injury, or disease.
- Familiarity with different types of transfusions and their purposes is essential for accurate documentation and coding.
3. Coding Instructions
Objective: Accurately code for transfusion treatment on admission. Key Points:
- Code '1' if any transfusion treatment was administered on the day of admission.
- Ensure the coding reflects actual transfusion treatment, verified through medical records, not just the physician's orders.
- Document all transfusion treatments administered on admission, regardless of the blood product type.
4. Coding Tips
Objective: Enhance accuracy in coding transfusion treatments. Key Points:
- Confirm the admission date and time against transfusion records to ensure accurate coding for transfusion treatment on admission.
- Clarify any ambiguous documentation with healthcare team members for accurate reflection of transfusion treatment.
- Understand that the coding of transfusion treatments is crucial for capturing the resident's clinical needs and the level of care provided on admission.
5. Documentation
Objective: Maintain comprehensive documentation for transfusion treatment. Key Points:
- Document specific details of the transfusion treatment administered on admission, including the type of blood product, dose, route, administration time, and indication.
- Include any adverse reactions or side effects noted following the transfusion in the resident's medical record.
- Ensure continuity of care by documenting any plans for additional transfusion treatments, including monitoring and follow-up requirements.
6. Common Errors to Avoid
Objective: Identify and correct frequent documentation and coding errors. Key Points:
- Not coding transfusion treatments administered on admission due to oversight or incomplete MARs.
- Confusing orders for transfusion with actual administration, leading to inaccurate coding if the treatment was not carried out.
- Failing to document the rationale for transfusion treatments and observed outcomes adequately.
7. Practical Application
Objective: Apply coding knowledge through real-world scenarios. Key Points:
- Scenario: A resident is admitted with severe anemia and receives a packed red blood cell transfusion shortly after admission. Detail the process of coding this scenario, emphasizing the importance of accurate treatment capture and documentation.
- Engage in case study discussions or simulations to practice identifying and coding transfusion treatments on admission.
- Review case studies in staff meetings, discussing the impact of accurate documentation and coding of transfusion treatments on admission and its significance for resident care planning.
Please note that the information provided in this guide for MDS 3.0 Item set
Please note that the information provided in this guide for MDS 3.0 Item set A0050 was originally based on the CMS's RAI Version 3.0 Manual, October 2023 edition. Every effort will be made to update it to the most current version. The MDS 3.0 Manual is typically updated every October. If there are no changes to the Item Set, there will be no changes to this guide. This guidance is intended to assist healthcare professionals, particularly new nurses or MDS coordinators, in understanding and applying the correct coding procedures for this specific item within MDS 3.0.
The guide is not a substitute for professional judgment or the facility’s policies. It is crucial to stay updated with any changes or updates in the MDS 3.0 manual or relevant CMS regulations. The guide does not cover all potential scenarios and should not be used as a sole resource for MDS 3.0 coding.
Additionally, this guide refrains from handling personal patient data and does not provide medical or legal advice. Users are responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations in their respective practices.
was originally based on the CMS's RAI Version 3.0 Manual, October 2023 edition. Every effort will be made to update it to the most current version. The MDS 3.0 Manual is typically updated every October. If there are no changes to the Item Set, there will be no changes to this guide. This guidance is intended to assist healthcare professionals, particularly new nurses or MDS coordinators, in understanding and applying the correct coding procedures for this specific item within MDS 3.0.
The guide is not a substitute for professional judgment or the facility’s policies. It is crucial to stay updated with any changes or updates in the MDS 3.0 manual or relevant CMS regulations. The guide does not cover all potential scenarios and should not be used as a sole resource for MDS 3.0 coding.
Additionally, this guide refrains from handling personal patient data and does not provide medical or legal advice. Users are responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations in their respective practices.